Wing Area Calculator
This wing area calculator allows you to compute the wing area for different types of aircraft wing designs. You can select between three types of wing shapes: rectangular, trapezoidal, and elliptical. The calculator uses the appropriate formula based on your selection and inputs the wingspan and chord measurements.
How the Wing Area Calculator Works
The following are the formulas used to calculate the wing area for different wing shapes:
- Rectangular Wing:
A = b × c
Wherebis the wingspan andcis the mean chord (average width). - Trapezoidal Wing:
A = (b × (c_root + c_tip)) / 2
Wherebis the wingspan,c_rootis the root chord, andc_tipis the tip chord. - Elliptical Wing:
A = (π / 4) × b × c
Wherebis the wingspan andcis the mean chord.
Here’s an example of how the calculator works for a rectangular wing:
- Given a wingspan of 20 inches and a mean chord of 5 inches, the area is calculated by multiplying these two values:
- Area = 20 × 5 = 100 square inches
This process is similar for other wing shapes, though the formulas differ slightly depending on whether the wing is rectangular, trapezoidal, or elliptical.
1. What is a rectangular wing?
A rectangular wing has a consistent chord (width) from the root to the tip. This type of wing is simple and easy to calculate, making it common for many basic aircraft designs.
2. What is a trapezoidal wing?
A trapezoidal wing has a wider root chord (near the aircraft body) and a narrower tip chord (at the wingtip). This type of wing design is often used for better aerodynamic performance and more efficient lift distribution.
3. What is an elliptical wing?
An elliptical wing is shaped like an ellipse, providing smooth airflow and efficient lift distribution. This type of wing is often seen in more advanced and high-performance aircraft.
4. Why is the wing area important?
The wing area is crucial for determining the amount of lift an aircraft can generate. Larger wings typically generate more lift, which is essential for supporting the weight of the aircraft during flight.
5. Can I use this calculator for all types of aircraft?
Yes! The calculator can be used for various aircraft types, as long as you know the wingspan and the chord measurements. Different wing shapes are commonly used in both small and large aircraft.
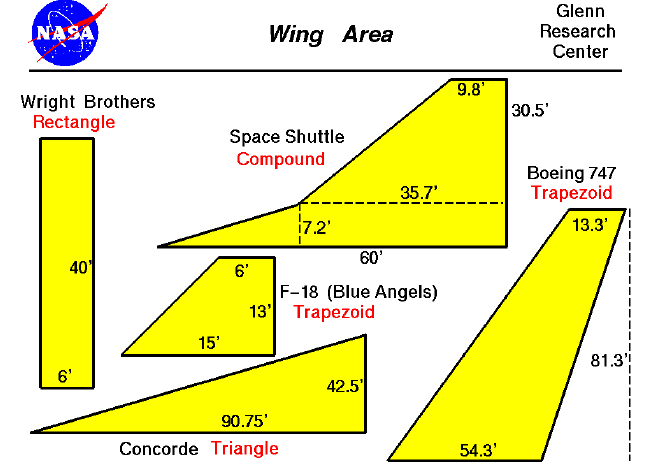
This calculator is based on the information from the NASA Glenn Research Center Virtual Aero website. The formulas and explanations for different wing shapes have been adapted from their educational resources.
When designing aircraft, the wing area is just one of many important factors that affect overall performance. Advanced calculations might consider other variables such as wing aspect ratio, airfoil shape, and the presence of winglets. These factors can significantly alter the lift-to-drag ratio and influence fuel efficiency and maneuverability.
In addition to the basic shape of the wing, aircraft engineers also consider:
- Wing Aspect Ratio: The ratio of the wingspan to the mean chord. A higher aspect ratio typically leads to lower drag and better lift efficiency.
- Winglets: Small extensions at the tips of the wings designed to reduce vortex drag and improve fuel efficiency.
- Airfoil Thickness: The thickness of the wing’s cross-section, which affects both lift generation and drag.
- Dihedral Angle: The upward angle of the wings relative to the fuselage, which improves the aircraft’s stability and performance in turns.
Modern aerospace designers use advanced simulation software and tools to model and optimize wing shapes for specific flight conditions. These tools often incorporate real-world variables such as turbulence, atmospheric pressure, and flight speed to give a more accurate prediction of an aircraft’s performance.
As aircraft design continues to evolve, engineers are exploring more advanced concepts such as morphing wings—wings that can change shape in-flight to optimize performance. These innovations are intended to improve fuel efficiency, reduce noise, and make air travel more sustainable.
Understanding and calculating wing area is fundamental to aircraft design, affecting everything from lift generation to overall aerodynamic efficiency. The tools provided, including the calculator and advanced design considerations, are crucial in making informed design decisions for both amateur enthusiasts and professional aerospace engineers.
Explore More Game Theory Tools
Want to explore more tools? Check out our full collection of Aerodynamics related calculators to enhance your learning and research.
Angle of attack related calculators