Boundary Layer Thickness Calculator
💡 Enjoying our free calculators?
Help us keep them running by grabbing some science-inspired merch on Redbubble! Every purchase supports the project 🙌 Grab your awesome stuff below!
How the Boundary Layer Thickness Calculator Works
This calculator estimates the boundary layer thickness for fluid flow over a flat plate, a crucial concept in fluid mechanics and aerodynamics.
Steps to Calculate Boundary Layer Thickness
- Select a fluid from the dropdown menu or enter a custom kinematic viscosity.
- Input the distance from the leading edge of the plate (x in meters).
- Input the free-stream velocity of the fluid (U∞ in m/s).
- Click "Calculate Thickness" to determine the boundary layer thickness.
- The calculator will indicate whether the flow is laminar or turbulent and provide the transition point.
Common Fluids and Their Kinematic Viscosity Values
| Fluid | Kinematic Viscosity (ν in m²/s) |
|---|---|
| Water (20°C) | 1.0 x 10-6 |
| Air (20°C) | 1.5 x 10-5 |
| Ethanol | 1.1 x 10-6 |
| Glycerin | 0.89 x 10-6 |
| Olive Oil | 1.0 x 10-3 |
| Vegetable Oil | 0.9 x 10-3 |
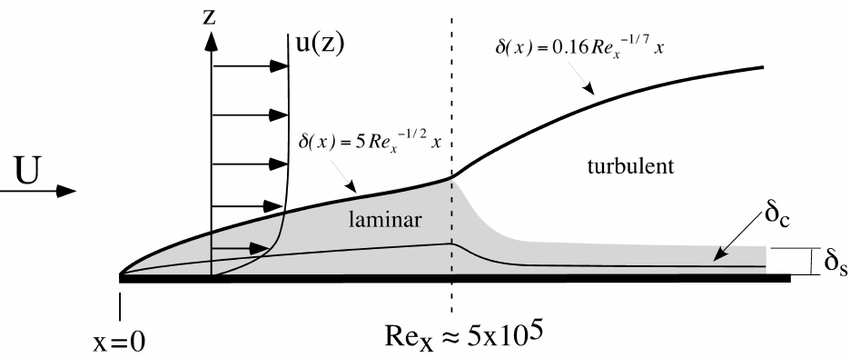
Boundary Layer Thickness Equations
The boundary layer thickness (δ) can be calculated using the following equations:
1. Laminar Flow
For laminar flow, the boundary layer thickness is given by:
δlaminar = 5 * √(ν * x / U∞)
Where:
- δlaminar = boundary layer thickness for laminar flow (m)
- ν = kinematic viscosity of the fluid (m²/s)
- x = distance from the leading edge of the plate (m)
- U∞ = free-stream velocity of the fluid (m/s)
2. Turbulent Flow
For turbulent flow, the boundary layer thickness is approximated as:
δturbulent = 0.37 * x * (Rex)-1/5
Where:
- δturbulent = boundary layer thickness for turbulent flow (m)
- Rex = Reynolds number, calculated as Rex = (U∞ * x) / ν
Note: This boundary layer thickness calculator is specifically designed for flow over a flat plate.